EUROWATER ma wieloletnie doświadczenie w uzdatnianiu wody pitnej. Robimy to od początku naszej działalności w roku 1936. Przez ten czas dostosowywaliśmy się do zmieniających przepisów i wymagań klientów. Nasze doświadczenie techniczne obejmuje uzdatnianie wody dla prywatnych ujęć wody, wodociągów publicznych i przemysłu.

Prywatne ujęcia wody
Wiele gospodarstw i domów mieszkalnych położonych jest poza obrębem lokalnych sieci wodociągowych. Uzdatnianie wody z ujęć prywatnych jest niezbędne, aby osiągnęła ona jakość wody pitnej.

Zakłady wodociągowe
Kompleksowe stacje uzdatniania wody EUROWATER zapewniają czystą wodę pitną 24/7/365 przy minimalnej obsłudze i bez użycia chemikaliów. Zapoznaj się z podstawami kompleksowych rozwiązań dla wody pitnej.

Firmy z własnymi ujęciami wody
Wiele firm posiada własne małe wodociągi. Uzdatnienie odpowiedniej ilości wody jest dla nich istotne w celu zachowania niezależności operacyjnej.
Dlaczego uzdatniamy wodę?
Zarówno woda gruntowa, jak i wody powierzchniowe zawierają naturalne sole, substancje organiczne, cząstki i gazy. Mogą one powodować między innymi zabarwienie, zły smak, rozwój bakterii w wodzie, a także korozję rurociągów i instalacji. EUROWATER ma wysokie kompetencje w usuwaniu szerokiego zakresu zanieczyszczeń.
Wybierz zanieczyszczenie i przeczytaj o dedykowanym rozwiązaniu
Aggressive carbon dioxideadd
Case
Aggressive carbon dioxide causes corrosion on concrete, pipe systems, and hot water storages in black steel. The corrosion products make the water indistinct and colours it red with corrosion and ochre.
The carbon dioxide is often present in raw water in areas with decalcified stratums of earth. The lack of calcium means that there is no neutralization of the carbon dioxide.
Solution
Aggressive carbon dioxide can be neutralized in a pressure filter plant by means of a calcium-based filter material called Magno-Dol. In special cases, aggressive carbon dioxide can be degassed by heavy aeration.
Ammoniumadd
Case
Ammonium can be a sign of microbacteriological activity in the water and can be a result of fertilization, contamination, or it can be geologically conditioned.
Solution
Ammonium can be reduced by a biological process, in which ammonium is transformed into nitrate via nitrite.
The process calls for a great oxygen demand and sufficient filter material consisting of quartz sand or a porous calcium-based filter material.
Arsenicadd
Case
Arsenic is a natural element and related to certain geochemical environments. Arsenic is found in two forms, As(III) and As(V), of which As(III) is more poisonous, harder to remove from the water, and more widespread.
WHO has assessed that arsenic forms a health risk when consumed and it is thought to be the reason for skin cancer, among other things.
The increased authority demands (lowering of the threshold limiting value from 50 to 5 µg/l when leaving the waterworks) affect many water supplies for which it will be necessary to carry out a special water treatment in order to keep the quality
requirements.
Possible solutions
If the limit value for arsenic in the drinking water is exceeded, a sensible and inexpensive solution is to optimize the water treatment. Arsenic is adhesive to iron and is filtered off with iron. In places without sufficient iron in the raw water for this process, the iron content of the water can be increased by adding iron chloride or iron sulphate and using iron oxide granulates as filter material.
This is an inexpensive solution to the arsenic problem and the method is used when there are small exceeding of the permitted arsenic content. However, this calls for sufficient filter capacity for this extra iron content.
Alternatively, arsenic can be reduced by adsorption filtration in a pressure filter with a special filter material based on iron hydroxide. Dosing with either iron chloride or iron sulphate and the use of iron oxide granulate as filter material are both water treatment solutions that is gaining a footing. EUROWATER offers both solutions and the choice depends on the actual conditions.
Bacteriaadd
Case
In order to measure the amount of bacteria in drinking water, the bacterial count is analyzed. This means the total number of bacteria found by culturing at 22°C and 37°C respectively.
At 22°C, there are bacteria which normally do not cause a disease. The bacterial count at 37°C indicates alien bacteria which often cause diseases. Thus, this count needs to be low. Micro-biological growth which is found in drinking water can consist of among other things bacteria, virus, algae, and fungus.
Solution
The bacteria can be effectively limited by ultraviolet light because micro-organisms are very sensitive to UV light. With a wavelength of 254 nm (nanometer), the UV light kills the bacteria, virus, algae, and fungus by breaking down the DNA of the micro-organisms. UV disinfection can be used for almost all water types.
Hardnessadd
Case
Groundwater often contain a high amount of calcium and magnesium salts which cause hardness in the water. Water softening remove the hardness and prevent scale from forming in pipe systems and plumbing.
Solution
If you require a certain amount of hardness in the water, nanofiltration can provide partial softening and without use of regeneration chemical. Removal of total hardness can be done by a softening unit.
Hydrogen, sulphide and methaneadd
Case
Hydrogen sulphide and methane are present many places in the groundwater and are formed by the decomposition of organic substances under oxygen-free conditions.
Both gasses give cause for different problems for a waterworks. Filters are clogged up by bacterial slime which reduces the content of oxygen and often, bad smell is also an indication of bacteria. In some cases, the bacteria can form hydrogen sulphide and methane.
It is important that all hydrogen sulphide and methane are removed because a residual amount of these gasses in the water will complicate the removal of iron and ammonium afterwards.
Solution
Both hydrogen sulphide and methane can be removed by heavy oxydation of the water. The oxydation takes place by aeration in order to add oxygen to the raw water.
Iron and manganeseadd
Case
Iron and manganese often cause the main problem of the waterworks' due to the substances' discolouring of the washing and sanitation at the consumer. Typical signs of increased iron and manganese content in the water are ochreous or dark water with a metallic taste.
Raw water can contain different types of iron dependent on where in the country you are. Sand filtration is thus not always sufficient. It may therefore be necessary to use other methods in order to ensure continuous iron-free water. These differences cannot be seen in the ordinary analyses but calls for know-how and experience to determine iron type and treatment method.
Solution
After the oxydation, iron and manganese can be filtered through sand filtration. The filter materials used for removing iron are Gravel lll and Nevtraco l.
For removing manganese, Hydrolit-Mn is used. Also, the filter media Demantex has proven to be a very efficient material for manganese removal, even under difficult conditions with low pH values where many other types of filter media are insufficient.
Pesticides, PFASadd
Case
Contamination from pesticides is primarily a result of the use of Caseron G and Prefix G for controlling weeds. The decomposition product 2.6-dichlorbenzamide - BAM - comes from dichlorbenil which forms part of Caseron and Prefix.
Today, waterworks bore wells are analysed for many different types of pesticides and pesticides are found in relatively many waterworks bore wells.
Solution
BAM can be reduced in a pressure filter with a filter material based on activated carbon. Activated carbon is a natural product made from stone, wood, or coconut shell. An activated carbon filter can among other things remove free chlorine, pesticides, and organic solution agents.
Sulphate, chloride, and fluorideadd
Solution
The content of sulphate, chloride, and fluoride in drinking water can be reduced by nanofiltration.
Nanofiltration is applied to purposively reduce unwanted components in full or in part. Nanofiltration applies a pressure typically under seven bar, resulting in lower energy consumption.
Nanofiltration is a membrane technology, which in its mode of operation and construction is very similar to reverse osmosis. A nanofiltration membrane primarily restrains divalent ions and larger molecules.
Redukcja zużycia wód gruntowych
NYE („nowe”) to nowe przedmieście w Aarhus w Danii, które jest „zorientowane” na oszczędność wody. 40% miejskiego zużycia wody jest pozyskiwane z wody deszczowej, która jest wykorzystana do spłukiwania toalet i prania.
Firma EUROWATER opracowała i wprowadziła system uzdatniania wody. Ten innowacyjny projekt to wynik ścisłej współpracy pomiędzy konsultantami, prywatnym deweloperem i lokalnymi wodociągami
Zielona technologia usuwa pestycydy
Obecność pestycydów w wodzie gruntowej stanowi rosnący problem. MEM2BIO to pilotażowy projekt, w którym naukowcy rozwijają ekologiczną technologię oczyszczania skażonej wody pitnej.
Połączenie dwóch dobrze znanych technologii: filtracji membranowej (MEM) oraz biofiltracji (BIO), ma duży potencjał. Firma EUROWATER zaprojektowała w tym celu pilotażową stację uzdatniania wody.
Naturalne procesy filtracji bez użycia chemikaliów
Filtry ciśnieniowe zaprojektowane przez EUROWATER wykorzystują do produkcji wody pitnej tylko naturalne procesy, takie jak napowietrzanie i filtracja. Dobre środowisko pracy i redukcja ścieków – to tylko niektóre korzyści z korzystania z rozwiązań EUROWATER.
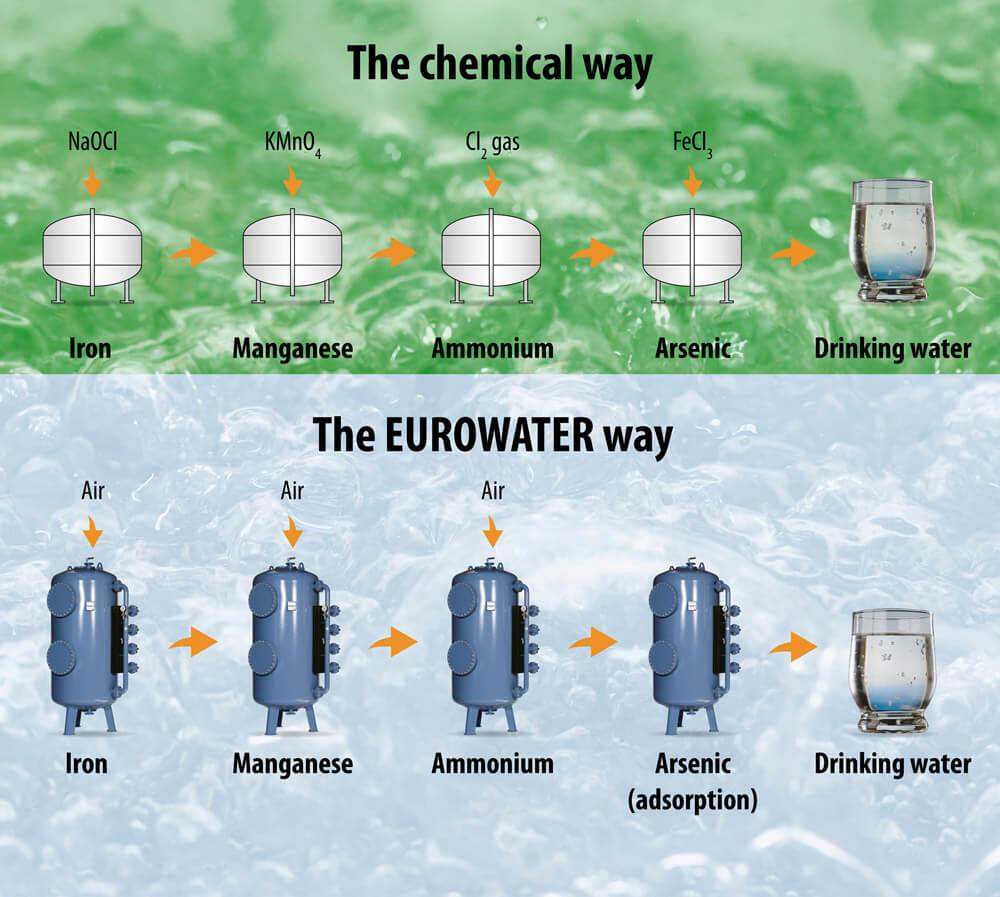
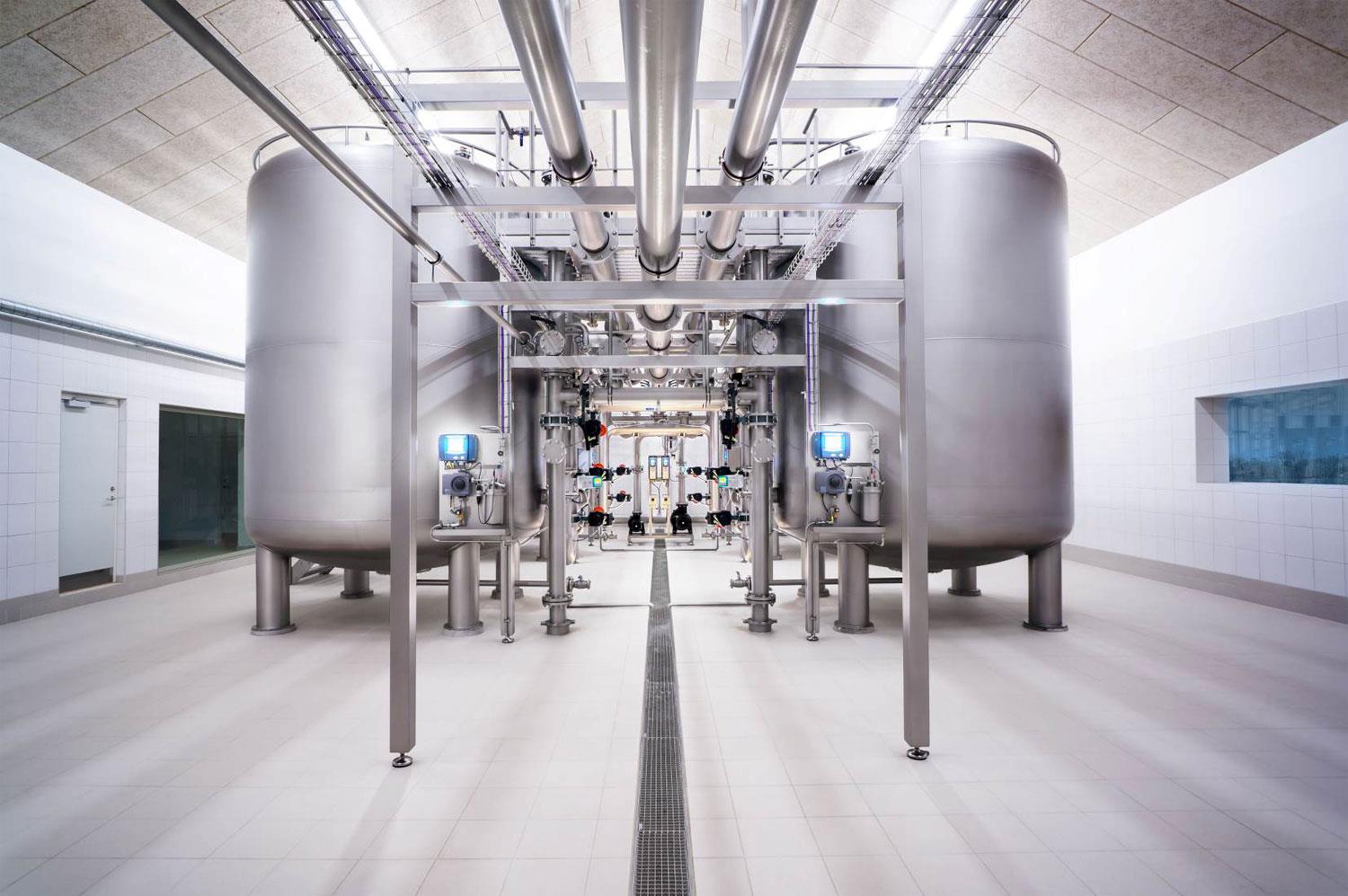
Kompleksowe rozwiązania dla wody pitnej
Bezpieczeństwo, niezawodność i automatyzacja – to główne cechy nowoczesnych systemów uzdatniania wody.
Dowiedz się więcej – ilustracje poniżej
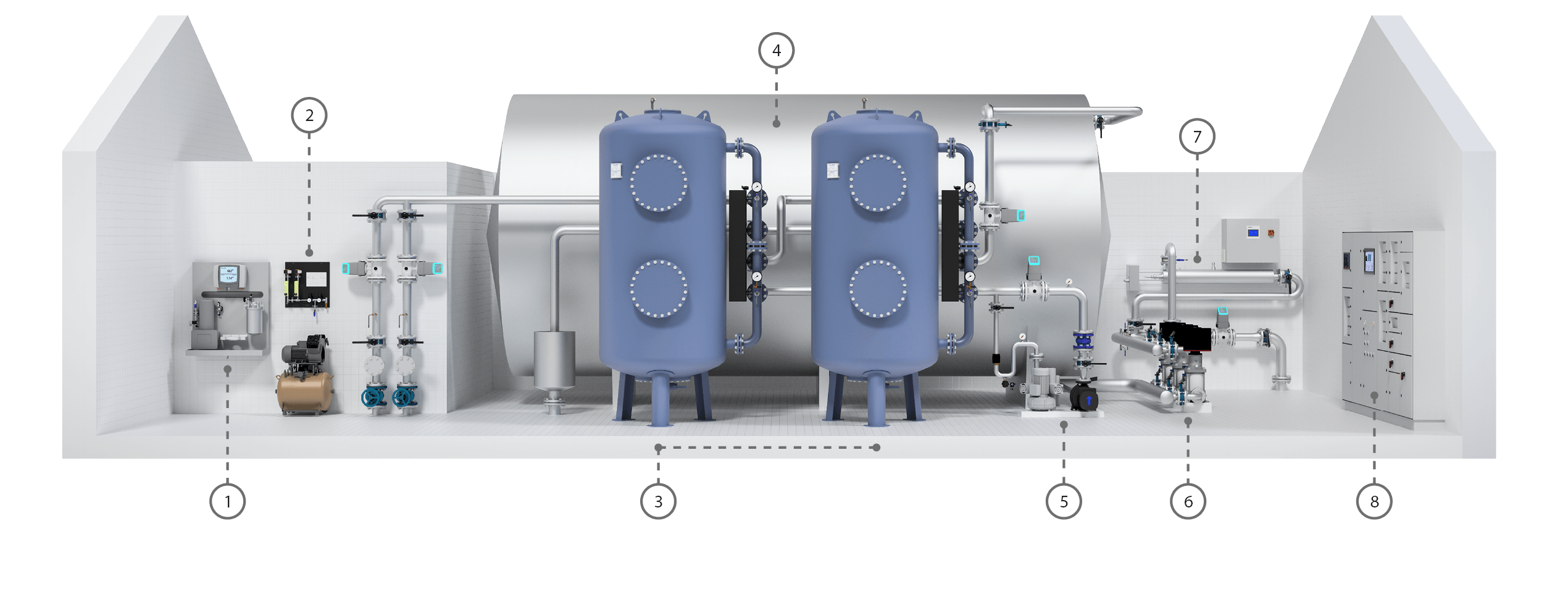
1. Analizator
Analizator do ciągłego pomiaru mętności, poziomu tlenu oraz temperatury. Pomaga w utrzymaniu niezawodnej pracy i zapewnia czystą wodę pitną.
2. Zestaw napowietrzający
Zestaw do napowietrzania składa się z kompresora i sterownika ilości powietrza.
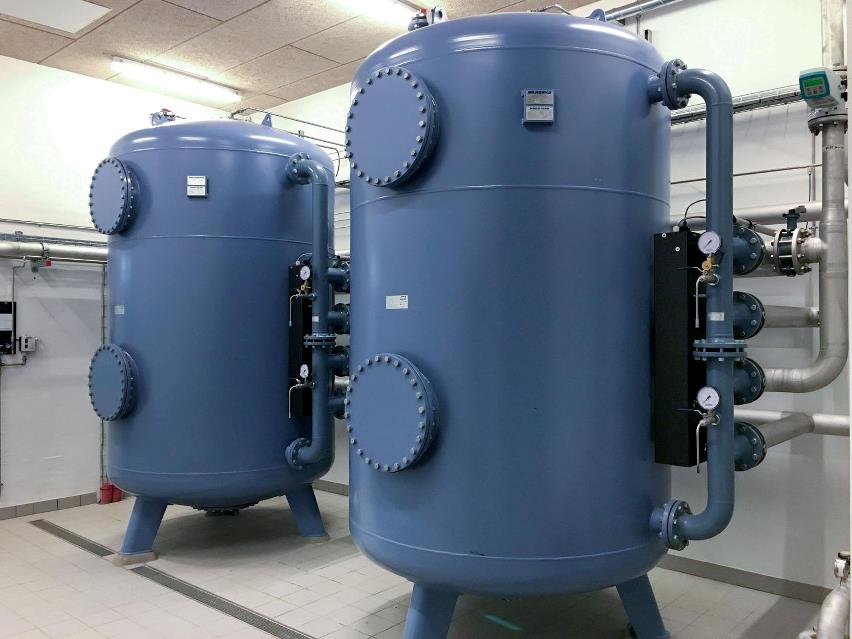
3. Filtry ciśnieniowe
W filtrze ciśnieniowym odbywa się napowietrzanie i filtracja. Woda jest napowietrzana, aby dostarczyć odpowiednią ilość tlenu potrzebną do spełnienia założonych kryteriów jakościowych. Dwa filtry ciśnieniowe mogą pracować jako dwie niezależne jednostki albo szeregowo.
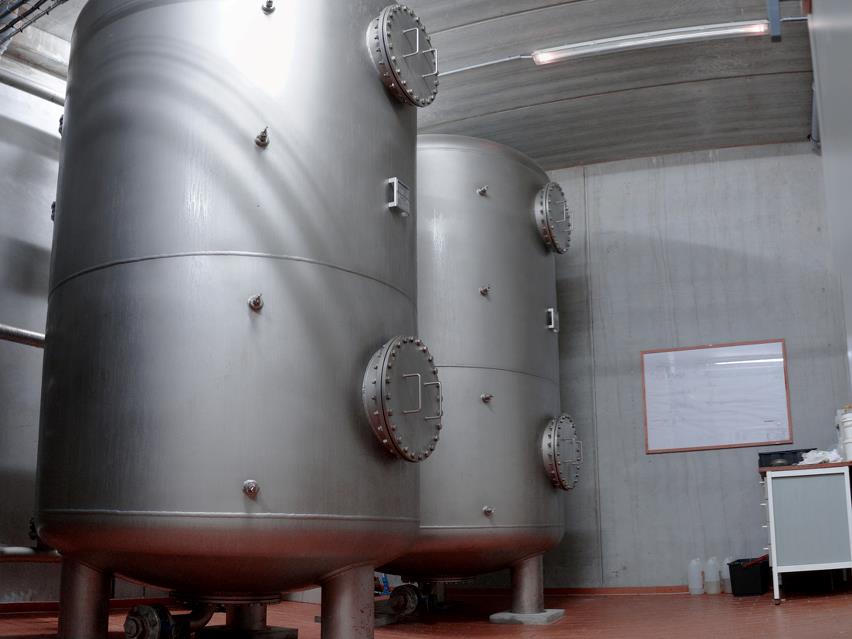
4. Zbiornik wody czystej
Po procesie napowietrzania i filtracji woda pitna jest magazynowana w zbiorniku wody czystej, zanim zostanie rozprowadzona do odbiorcy.
5. Dmuchawa i pompa płucząca do płukania wstecznego
Substancje, które są zatrzymywane w filtrze, są usuwane w procesie płukania wstecznego. Częstotliwość, intensywność oraz czas trwania płukania są programowane w zależności od potrzeb.
6. Dystrybucja
Rozprowadzenie wody odbywa się przy pomocy zestawu pompowego z falownikiem.
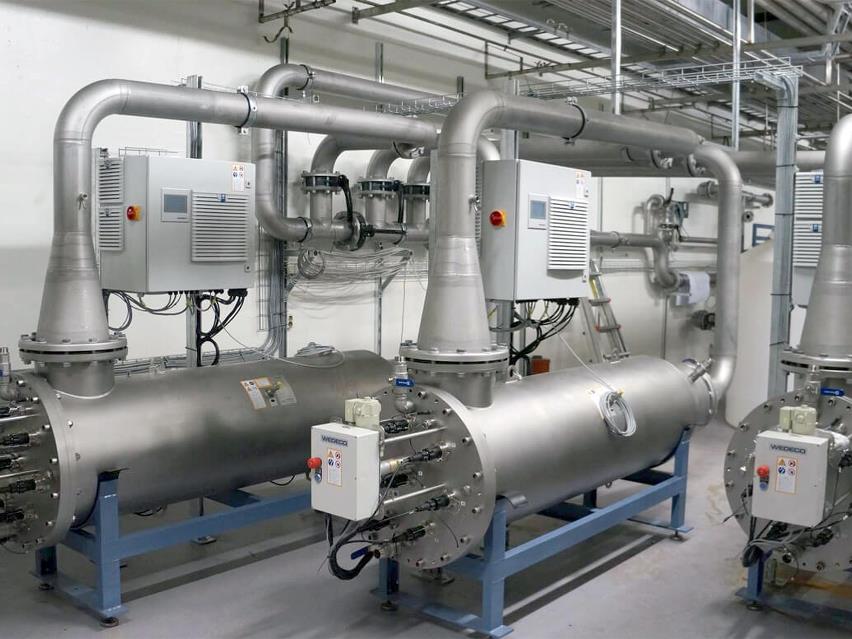
7. Dezynfekcja UV
Dezynfekcja UV w wydajny sposób redukuje rozwój mikroorganizmów w wodzie. Proces ten zapewnia bezpieczeństwo oraz czystość wody pitnej.
8. Sterowanie
Cały proces jest sterowany, regulowany i kontrolowany poprzez sterownik (SRO/PLC).
Technologie używane do uzdatniania wody pitnej
Produkcja wody pitnej wymaga zastosowania wielu technologii w zależności od składu wody surowej.
Wybraliśmy trzy najpowszechniejsze technologie do produkcji czystej wody pitnej.
Dezynfekcja UV
Wysoka jakość wody pitnej jest kluczowa. Dezynfekcja UV jest dodatkową barierą bezpieczeństwa w produkcji czystej wody pitnej, ponieważ pozwala wyeliminować ryzyko skażenia wody pitnej mikroorganizmami.
Węgiel aktywny
W wielu krajach woda pitna jest dezynfekowana przy użyciu chloru. Bardzo ważne jest, aby usunąć wolny chlor dla zapewnienia czystości wody pitnej. Węgiel aktywny może być również używany do usuwania pestycydów, które mogą być obecne w wodzie gruntowej.
Zobacz filtry z węglem aktywnym
Filtry ciśnieniowe
Filtry ciśnieniowe EUROWATER to bezpieczny i wolny od chemikaliów sposób, aby uzyskać czystą wodę pitną, wolną od żelaza, manganu, amoniaku i substancji agresywnych.
Referencje
Uzdatnianie wody pitnej
Jak możemy ci pomóc?
Nasi specjaliści chętnie odpowiedzą na twoje pytania na temat uzdatniania wody.




