EUROWATER has years of experience with drinking water production. We have gone all the way and have adapted to changing statutory requirements and demands from our customers - and we have done it since 1936. Our know-how covers both private water supply, municipal waterworks and industries with their own water supply.

Private water supply
Many farms and houses are located so a connection to a bigger, municipal waterworks is unsuitable. A private water treatment solution is therefore necessary to attain drinking water quality.

Municipal waterworks
A complete water treatment solution from EUROWATER is chemical-free, easy to operate and ensures pure drinking water 24/7/365. Get an introduction to a complete drinking water solution.

Companies with their own water supply
Many companies establish their own small waterworks. To get the amount of treated water that is required for keeping operational reliability.
Why treat water?
Both groundwater and surface water contain several natural salts and organic substances, particles, and gasses. They can be the reason for colour, bad taste, bacteria in the water and corrosion in pipes and installations among other things. EUROWATER has extensive experience with removal of a wide range of impurities.
Choose impurity and see specific treatment method
Aggressive carbon dioxideadd
Case
Aggressive carbon dioxide causes corrosion on concrete, pipe systems, and hot water storages in black steel. The corrosion products make the water indistinct and colours it red with corrosion and ochre.
The carbon dioxide is often present in raw water in areas with decalcified stratums of earth. The lack of calcium means that there is no neutralization of the carbon dioxide.
Solution
Aggressive carbon dioxide can be neutralized in a pressure filter plant by means of a calcium-based filter material called Magno-Dol. In special cases, aggressive carbon dioxide can be degassed by heavy aeration.
Ammoniumadd
Case
Ammonium can be a sign of microbacteriological activity in the water and can be a result of fertilization, contamination, or it can be geologically conditioned.
Solution
Ammonium can be reduced by a biological process, in which ammonium is transformed into nitrate via nitrite.
The process calls for a great oxygen demand and sufficient filter material consisting of quartz sand or a porous calcium-based filter material.
Arsenicadd
Case
Arsenic is a natural element and related to certain geochemical environments. Arsenic is found in two forms, As(III) and As(V), of which As(III) is more poisonous, harder to remove from the water, and more widespread.
WHO has assessed that arsenic forms a health risk when consumed and it is thought to be the reason for skin cancer, among other things.
The increased authority demands (lowering of the threshold limiting value from 50 to 5 µg/l when leaving the waterworks) affect many water supplies for which it will be necessary to carry out a special water treatment in order to keep the quality
requirements.
Possible solutions
If the limit value for arsenic in the drinking water is exceeded, a sensible and inexpensive solution is to optimize the water treatment. Arsenic is adhesive to iron and is filtered off with iron. In places without sufficient iron in the raw water for this process, the iron content of the water can be increased by adding iron chloride or iron sulphate and using iron oxide granulates as filter material.
This is an inexpensive solution to the arsenic problem and the method is used when there are small exceeding of the permitted arsenic content. However, this calls for sufficient filter capacity for this extra iron content.
Alternatively, arsenic can be reduced by adsorption filtration in a pressure filter with a special filter material based on iron hydroxide. Dosing with either iron chloride or iron sulphate and the use of iron oxide granulate as filter material are both water treatment solutions that is gaining a footing. EUROWATER offers both solutions and the choice depends on the actual conditions.
Bacteriaadd
Case
In order to measure the amount of bacteria in drinking water, the bacterial count is analyzed. This means the total number of bacteria found by culturing at 22°C and 37°C respectively.
At 22°C, there are bacteria which normally do not cause a disease. The bacterial count at 37°C indicates alien bacteria which often cause diseases. Thus, this count needs to be low. Micro-biological growth which is found in drinking water can consist of among other things bacteria, virus, algae, and fungus.
Solution
The bacteria can be effectively limited by ultraviolet light because micro-organisms are very sensitive to UV light. With a wavelength of 254 nm (nanometer), the UV light kills the bacteria, virus, algae, and fungus by breaking down the DNA of the micro-organisms. UV disinfection can be used for almost all water types.
Hardnessadd
Case
Groundwater often contain a high amount of calcium and magnesium salts which cause hardness in the water. Water softening remove the hardness and prevent scale from forming in pipe systems and plumbing.
Solution
If you require a certain amount of hardness in the water, nanofiltration can provide partial softening and without use of regeneration chemical. Removal of total hardness can be done by a softening unit.
Hydrogen, sulphide and methaneadd
Case
Hydrogen sulphide and methane are present many places in the groundwater and are formed by the decomposition of organic substances under oxygen-free conditions.
Both gasses give cause for different problems for a waterworks. Filters are clogged up by bacterial slime which reduces the content of oxygen and often, bad smell is also an indication of bacteria. In some cases, the bacteria can form hydrogen sulphide and methane.
It is important that all hydrogen sulphide and methane are removed because a residual amount of these gasses in the water will complicate the removal of iron and ammonium afterwards.
Solution
Both hydrogen sulphide and methane can be removed by heavy oxydation of the water. The oxydation takes place by aeration in order to add oxygen to the raw water.
Iron and manganeseadd
Case
Iron and manganese often cause the main problem of the waterworks' due to the substances' discolouring of the washing and sanitation at the consumer. Typical signs of increased iron and manganese content in the water are ochreous or dark water with a metallic taste.
Raw water can contain different types of iron dependent on where in the country you are. Sand filtration is thus not always sufficient. It may therefore be necessary to use other methods in order to ensure continuous iron-free water. These differences cannot be seen in the ordinary analyses but calls for know-how and experience to determine iron type and treatment method.
Solution
After the oxydation, iron and manganese can be filtered through sand filtration. The filter materials used for removing iron are Gravel lll and Nevtraco l.
For removing manganese, Hydrolit-Mn is used. Also, the filter media Demantex has proven to be a very efficient material for manganese removal, even under difficult conditions with low pH values where many other types of filter media are insufficient.
Pesticides, PFASadd
Case
Contamination from pesticides is primarily a result of the use of Caseron G and Prefix G for controlling weeds. The decomposition product 2.6-dichlorbenzamide - BAM - comes from dichlorbenil which forms part of Caseron and Prefix.
Today, waterworks bore wells are analysed for many different types of pesticides and pesticides are found in relatively many waterworks bore wells.
Solution
BAM can be reduced in a pressure filter with a filter material based on activated carbon. Activated carbon is a natural product made from stone, wood, or coconut shell. An activated carbon filter can among other things remove free chlorine, pesticides, and organic solution agents.
Sulphate, chloride, and fluorideadd
Solution
The content of sulphate, chloride, and fluoride in drinking water can be reduced by nanofiltration.
Nanofiltration is applied to purposively reduce unwanted components in full or in part. Nanofiltration applies a pressure typically under seven bar, resulting in lower energy consumption.
Nanofiltration is a membrane technology, which in its mode of operation and construction is very similar to reverse osmosis. A nanofiltration membrane primarily restrains divalent ions and larger molecules.
Reduce groundwater extraction
NYE ('new'), a new suburb in Aarhus, Denmark, is a waterwise suburb. 40 % of the water consumption is covered by rain water harvesting and reused for toilet flushing and washing machines.
EUROWATER has developed and established the water treatment solution. This radical urban development project is a close cooperation between consultants, private developer and local water utility.
Green technology removes pesticides
Pesticides in ground water is an increasing problem. MEM2BIO is a pilot project where researchers will develop a green technology for cleaning contaminated drinking water.
Combining the two well-known technologies MEMbrane filtration and BIOfiltration is showing great potential. EUROWATER has designed the pilot water treatment plant.
A natural process without chemicals
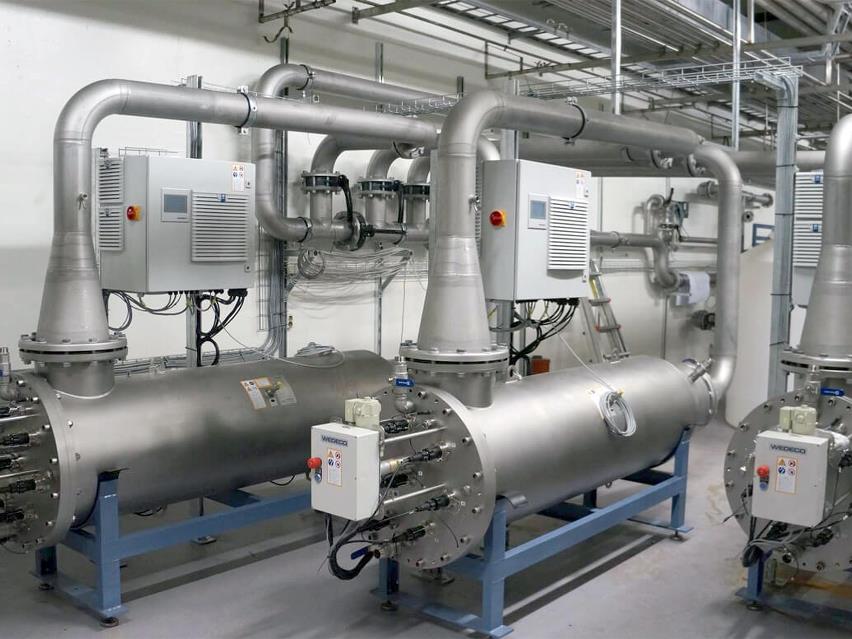
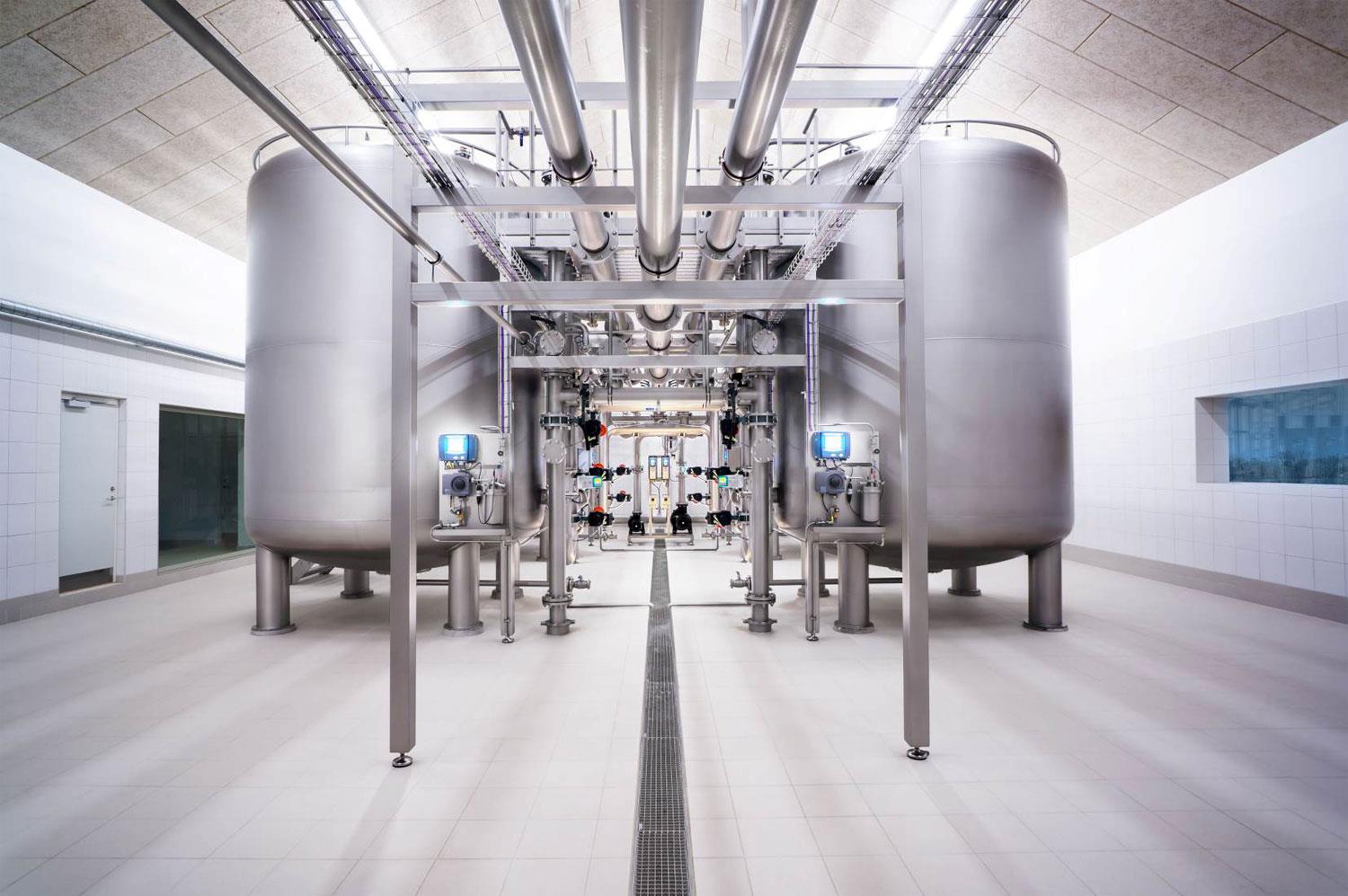
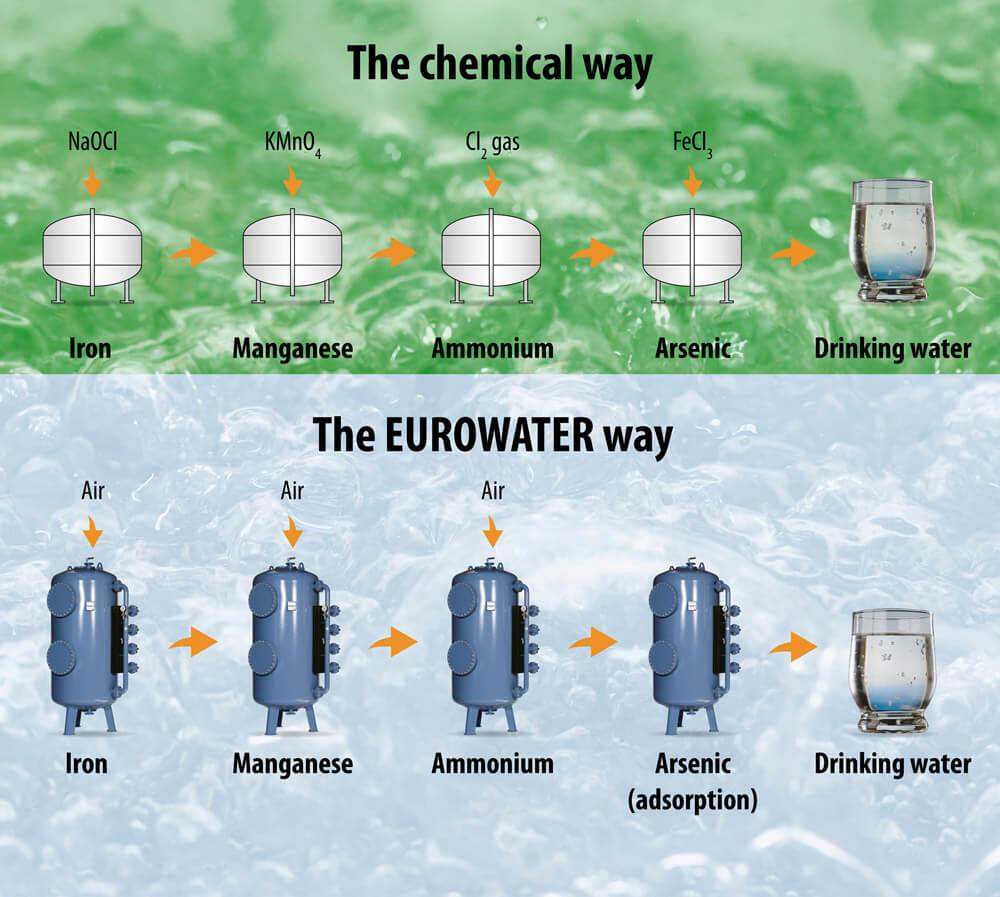
Pressure filters from EUROWATER are designed to use only a natural process such as oxidation and filtration for producing drinking water. Good work environment and no wastewater problems are some of the benefits of the EUROWATER way.
A complete drinking water solution
Safety, reliable operation and automation describes a modern water treatment solution.
Learn more in the illustration below.
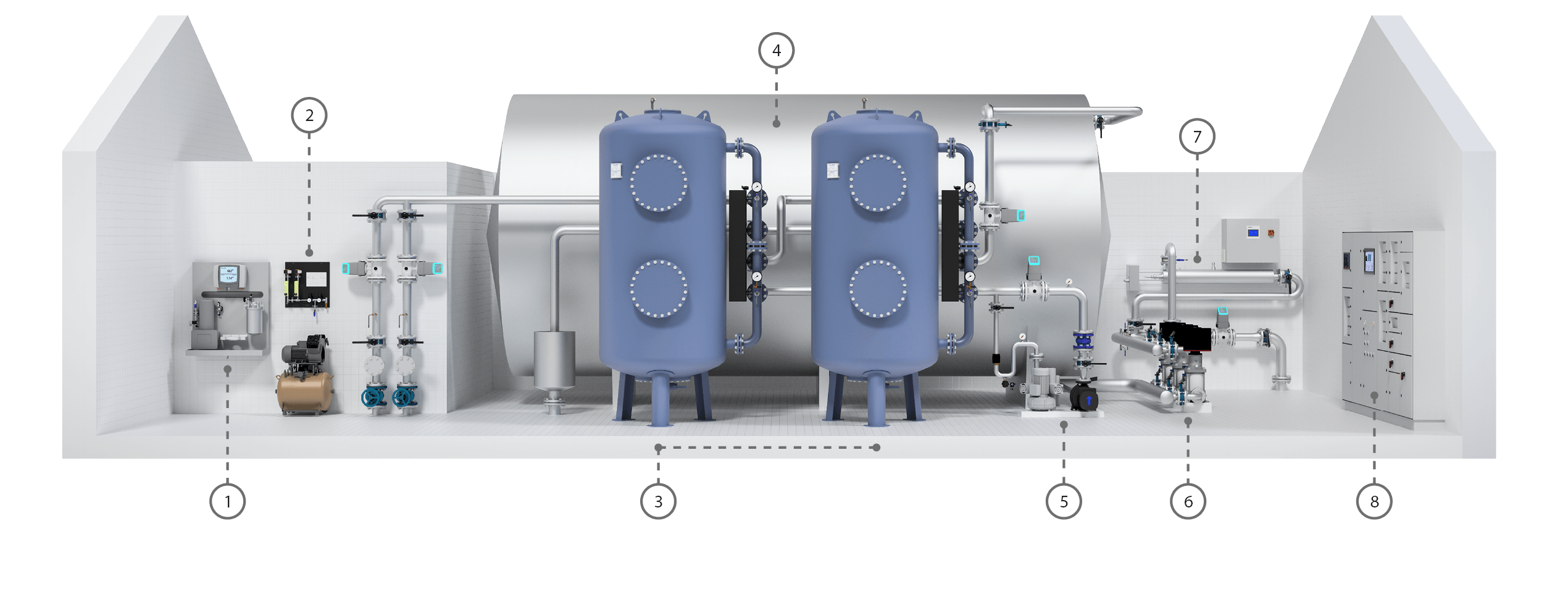
1. Analyzer
The analyzer helps maintain a reliable operation and ensure pure drinking water by providing an online measurement of turbidity, oxygen and temperature.
2. Aeration equipment
The aeration equipment consists of a compressor unit and a control air system. Aeration is a vital part of the treatment, as it ensures conditions for the oxidation of targeted contaminants inside the following pressure filters.
3. Pressure filter
Oxidation and filtration occur inside the pressure filter. The water is aerated at the top section of the vessel and then filtered along with the filter depth. The filter can have several filter materials which are selected to promote the removal of specific contaminants. The two pressure filters can act as two independent production lines or connected in series if further filtration is required.
4. Clean water tank
After the oxidation and filtration, the drinking water is stored in a clean water tank before it is distributed to the consumer.
5. Blower and rinse pump for backwash
The substances retained in the filter are removed by a backwash procedure. Depending on the accumulation of particles and filter material selected for the pressure filters, the backwash is defined with regards to frequency, intensity, and duration.
6. Distribution
The distribution takes places by means of a frequency-controlled pumping plant.
7. UV disinfection
UV disinfection can efficiently reduce microbiological growth in water. This ensures safe and clean drinking water.
8. Control
The entire process is controlled, regulated, and monitored centrally from an automatic control system (SRO/PLC).
Technologies used for drinking water treatment
Drinking water production require a number of technologies depending on the composition of the raw water.
We have selected three of the most common technologies for production of pure drinking water.
UV disinfection
High quality drinking water is vital and UV disinfection is an extra security measure to ensure clean drinking water by eliminating the risk of microbiological contamination.
Activated carbon
In many countries, drinking water is disinfected by adding chlorine. It is important to remove free chlorine to ensure clean drinking water. Activated carbon can also be used for removal of pesticides which can be found in groundwater.
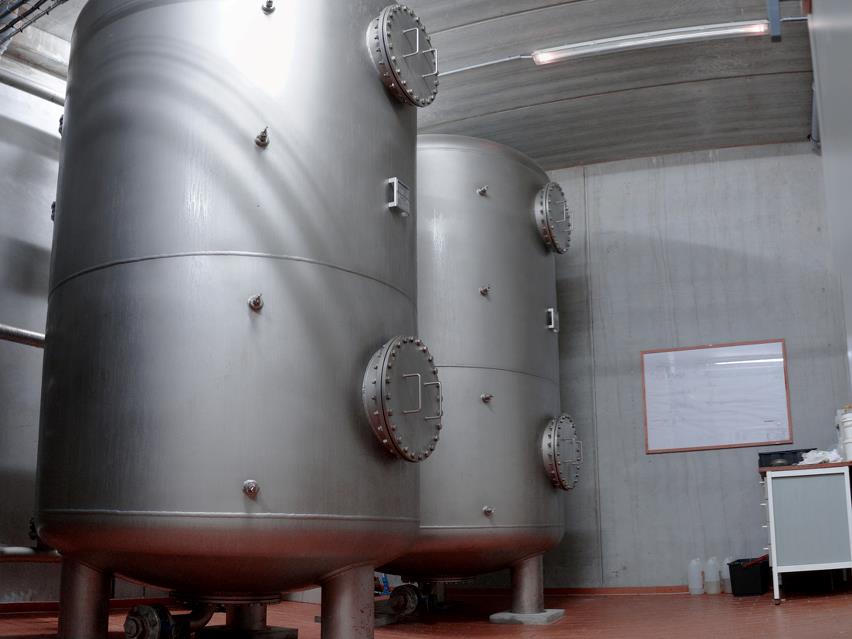
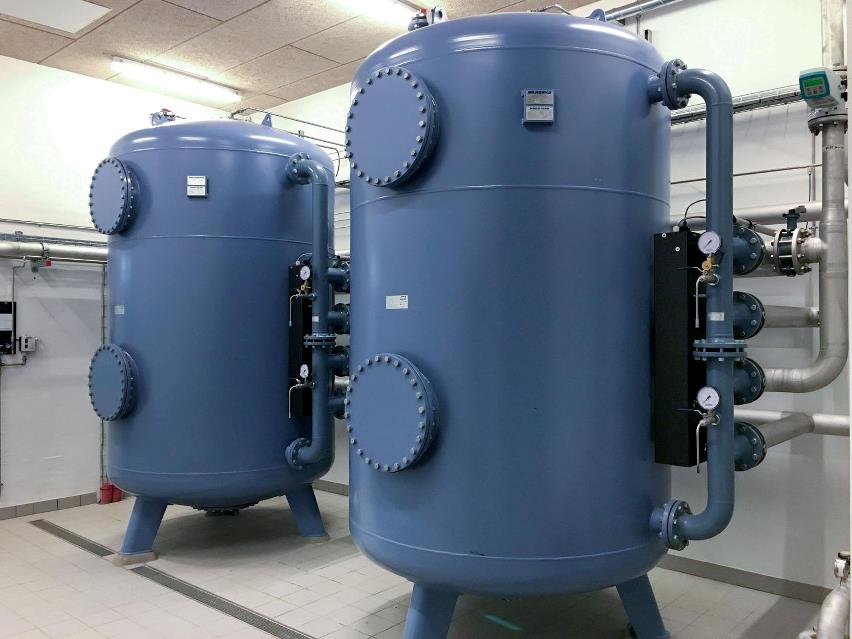
Pressure filter
A EUROWATER pressure filter is a safe and chemical-free solution to attain clean drinking water by removing iron, manganese, ammonium, and aggressivity.
References
Drinking water treatment
How can we help?
Our team of specialists are ready to answer your questions about pure water treatment solutions.




